VOA慢速英语 2008 0515b
搜索关注在线英语听力室公众号:tingroom,领取免费英语资料大礼包。
(单词翻译)
THE MAKING OF A NATION - US History: Adams Avoids War With France, Signs Alien and Sedition1 Acts
Two major issues marked John Adams' presidency2: foreign policy and the rights of citizens. At the same time, his Federalist Party was losing public support. Transcript3 of radio broadcast:
14 May 2008
Welcome to THE MAKING OF A NATION – an American history series in VOA Special English. This week on our program, we continue the story of America's second president, John Adams. Here are Maurice Joyce and Richard Rael.
VOICE TWO:
 |
| John Adams, by the American sculptor4 Daniel Chester French (1850-1931) |
John Adams took office in seventeen ninety-seven. He had served eight years as vice5 president under President George Washington. Now, state electors had chosen him to govern the new nation.
Adams was an intelligent man. He was a true patriot6 and an able diplomat7. But he did not like party politics. This weakness caused trouble during his presidency. For, during the late seventeen hundreds, two political parties struggled for power. He was caught in the middle.
VOICE ONE:
Adams was a member of the Federalist Party. As president, he should have been party leader. But this position belonged to a man who really knew how to get and use political power, Alexander Hamilton. Hamilton served as treasury8 secretary under President Washington. Now, he was a private citizen, a lawyer in New York City.
Through the Federalist Party, Hamilton continued to have great influence over the national government. Federalists loyal to Hamilton controlled the Congress. Even President Adams' three cabinet ministers were loyal to Hamilton. In fact, they worked together against the new president.
 |
| Alexander Hamilton |
This political situation made Adams' term in office very difficult. Yet strangely, it also led to the end of Federalist Party power.
VOICE TWO:
Two major issues marked Adams' presidency. One concerned foreign policy. The other concerned the rights of citizens.
The first involved America's relations with France.
Federalists, in general, were men of wealth and position. They did not believe in democracy, rule by the people. For this reason, they strongly opposed the revolution in France. They were horrified9 by the execution of the French king and queen. Federalists wanted an alliance with Britain. Over time, they demanded war with France.
(MUSIC)
VOICE ONE:
American support for France came from the opposition10 party, the Republicans. The leader of that party was the country's vice president, Thomas Jefferson.
France helped America win its war for independence from Britain. The friendship formed during the war continued afterward11 when Thomas Jefferson served as Minister to Paris. Relations began to turn bad as soon as he returned home.
The man who replaced him openly supported the French monarchy12 -- the losing side in the revolution. After the revolution succeeded, the new French government demanded that he leave.
VOICE TWO:
Most Federalists did not want good relations with France. They used their power to prevent the government from sending a pro-French representative to Paris. They also searched for any signs of insult, any excuse to declare war.
President Adams did not agree with the majority of Federalists. He wanted to improve relations with France through negotiations13. Yet he said the United States would strengthen its defenses. We will be ready, he said, if war comes.
VOICE ONE:
One incident, especially, brought the two nations close to war. It is known in American history books as the "X, Y and Z Affair."
President Adams had appointed a committee of three ministers to negotiate with the French government. French officials kept these three men waiting for several weeks. While they waited, they had a visit from three Frenchmen -- later called X, Y and Z.
X, Y and Z told the Americans that France would sign an agreement if the United States did three things.
It had to lend the French government twelve million dollars. It had to apologize for anti-French statements in a recent message from President Adams to the American Congress. And it had to pay the French foreign minister two hundred fifty thousand dollars.
VOICE TWO:
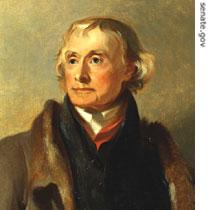 |
| Thomas Jefferson |
The American ministers were willing to pay. But they wanted to sign the agreement first. The French foreign minister refused. First the money, then the agreement.
The Federalists finally had the excuse they were looking for. France had insulted the United States. We must answer the insult. The only answer was war. Federalist newspapers added fuel to the fire by publishing anti-French propaganda. In a few places, pro-war groups became violent.
The Republican Party could do little. Even Thomas Jefferson was helpless. He remained in Philadelphia, the capital of the United States at that time. But he had few friends there anymore.
(MUSIC)
VOICE ONE:
Congress quickly passed laws to create a permanent army and navy. It also approved new taxes to pay for them.
Two new laws passed by a small vote. But they greatly increased the powers of the national government. The laws were known as the Alien and Sedition Acts. Federalists said they were necessary to protect national security. But, in effect, the Federalists used them to weaken the power of the Republican Party.
VOICE TWO:
 |
| The Alien and Sedition Acts tightened14 restrictions15 on foreigners and limited speech critical of government. Both measures were passed in preparation for a possible war with France. |
Under the Alien Act, the president could accuse any foreigner living in the United States of being a threat to national security. He could order that person out of the country.
The act also increased the time a foreigner had to wait to become a citizen, from five years to fourteen years.
Republicans were furious. Most foreigners, when they became naturalized citizens, joined the Republican Party.
Republicans argued that the Alien Act violated the Constitution. They said it gave the government more powers than were stated in the Constitution. Federalists said the act was Constitutional. They said the Constitution gave the government the right to defend the country against foreign aggression16.
VOICE ONE:
The other law, the Sedition Act, barred the publication of anything that might incite17 public hostility18 against the government.
Republicans argued that this act violated Americans' Constitutional rights of free speech and a free press. Federalists, once again, defended it as necessary for national security.
The Federalists tried to use the Sedition Act to quiet Republican critics of President Adams' administration. About twenty-five persons were charged under the Sedition act. These included several leading Republican newspapermen and a Republican member of Congress.
Some of the men were tried and found guilty and sent to prison. But other Republicans took their places in the fight against the act. The Federalist plan to stop criticism did not succeed.
VOICE TWO:
President Adams had signed the Alien and Sedition Acts into law. He believed they were necessary to protect the United States at a time when war with France was still possible.
Then, in early seventeen ninety-nine, Adams received several reports that France was ready to reopen negotiations on improving relations. He immediately nominated a new minister to France. Federalist senators threatened to reject the nomination19. In the end, Adams agreed to nominate a committee of three ministers. The Senate approved them.
VOICE ONE:
It was many months before the three men went to France to negotiate the agreement. And it was many more months before they completed their work. But they did so on September thirtieth, eighteen hundred.
After several years of bitter political struggle at home, President Adams finally prevented war with France. Later he wrote: "There is one thing I would like to be remembered for more than anything else. I gave myself the task of making peace with France. And I succeeded."
VOICE TWO:
The year eighteen hundred was another presidential election year in the United States. The Federalist Party appeared to be dying. It failed in its effort to force the nation into war with France. And it failed to silence its critics through the Alien and Sedition Acts. Party leaders knew the election would be their last chance to keep political power.
The Republican Party had more popular support. It also had gained an increasing number of seats in state legislatures and the national Congress. Party leader Thomas Jefferson was sure to be elected president -- unless the Federalists could find a way to change the electoral process.
That will be our story next week.
(MUSIC)
ANNOUNCER:
Our program was written by Christine Johnson. The narrators were Maurice Joyce and Richard Rael. Join us again for THE MAKING OF A NATION, an American history series in VOA Special English. Next week our subject will be the election of eighteen hundred. Transcripts20, podcasts and MP3s of our programs can be found at voaspecialenglish.com.
 收听单词发音
收听单词发音 




