Cloning has always been with us and is here to stay. It is a way of making an exact copy of another animal or plant. It happens in plants when gardeners take cuttings from growing plants to make new ones. It also happens in animals when twins identical in sex and appearance are produced from the same original egg. The fact is that these are both examples of natural clones.
Cloning has two major uses. Firstly, gardeners use it all the time to produce commercial quantities of plants. Secondly1, it is valuable for research on new plant species and for medical research on animals. Cloning plants is straightforward2 while cloning animals is very complicated. It is a difficult task to undertake. Many attempts to clone mammals failed. But at last the determination and patience of the scientists paid off in 1996 with a breakthrough - the cloning of Dolly the sheep. The procedure works like this:
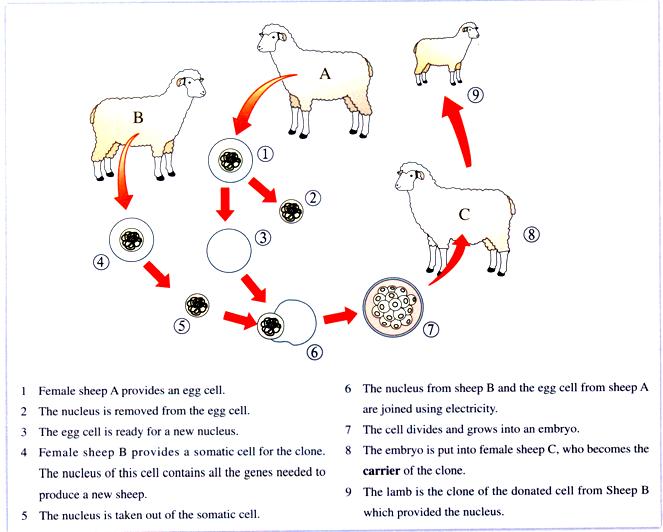
On the one hand, the whole scientific world followed the progress of the first successful clone, Dolly the sheep. The fact that she seemed to develop normally was very encouraging. Then came the disturbing news that Dolly had become seriously ill. Cloning scientists were cast down to find that Dolly's illnesses were more appropriate to a much older animal. Altogether Dolly lived six and a half years, half the length of the life of the original sheep. Sadly the same arbitrary fate affected3 other species, such as cloned mice. The questions that concerned all scientists were: "Would this be a major difficulty for all cloned animals? Would it happen forever? Could it be solved if corrections were made in their research procedure?"
On the other hand, Dolly's appearance raised a storm of objections and had a great impact on the media and public imagination. It became controversial. It suddenly opened everybody's eyes to the possibility of using cloning to cure serious illnesses and even to produce human beings.
Although at present human egg cells and embryos4 needed for cloning research are difficult to obtain, newspapers wrote of evil leaders hoping to clone themselves to attain5 their ambitions. Religious leaders also raised moral questions. Governments became nervous and more conservative. Some began to reform their legal systems and forbade research into human cloning, but other countries like China and the UK, continued to accumulate evidence of the abundant medical aid that cloning could provide. However, scientists still wonder whether cloning will help or harm us and where it is leading us
点击

收听单词发音
1
secondly

|
|
| adv.第二,其次 |
参考例句: |
- Secondly,use your own head and present your point of view.第二,动脑筋提出自己的见解。
- Secondly it is necessary to define the applied load.其次,需要确定所作用的载荷。
|
2
straightforward

|
|
| adj.正直的,坦率的;易懂的,简单的 |
参考例句: |
- A straightforward talk is better than a flowery speech.巧言不如直说。
- I must insist on your giving me a straightforward answer.我一定要你给我一个直截了当的回答。
|
3
affected

|
|
| adj.不自然的,假装的 |
参考例句: |
- She showed an affected interest in our subject.她假装对我们的课题感到兴趣。
- His manners are affected.他的态度不自然。
|
4
embryos

|
|
| n.晶胚;胚,胚胎( embryo的名词复数 ) |
参考例句: |
- Somatic cells of angiosperms enter a regenerative phase and behave like embryos. 被子植物体细胞进入一个生殖阶段,而且其行为象胚。 来自辞典例句
- Evolution can explain why human embryos look like gilled fishes. 进化论能够解释为什么人类的胚胎看起来象除去了内脏的鱼一样。 来自辞典例句
|
5
attain

|
|
| vt.达到,获得,完成 |
参考例句: |
- I used the scientific method to attain this end. 我用科学的方法来达到这一目的。
- His painstaking to attain his goal in life is praiseworthy. 他为实现人生目标所下的苦功是值得称赞的。
|

 收听单词发音
收听单词发音 





















